A New Practical Design of Super Point Cooling for Die Castings
Abstract: aiming at the problem of common super point cooling caused by the space limitation of die casting structure, a new super point cooling method was proposed, which can expand the space of point cooling and solve the defects such as burns and shrinkage holes in the partial small position of the product, thus improving the qualified rate of the product.
Under the trend of energy saving and emission reduction, the automobile lightweight has attracted more and more attention. Using aluminum alloys instead of steel structure, the development of traditional automobile lightweights and new energy vehicles have been more and more applied. A die casting mould as the key tool in die casting process, its effective life is very important to reduce the product cost. Thermal alternating stress fatigue caused by the temperature imbalance of the forming surface of the die is the main factor of die failures.
1. The way to solve the temperature imbalance
(1) For die castings, the temperature difference is reduced by effective output of input energy (The energy emitted by the aluminum alloy melt with temperatures from 650℃±10℃ to 200℃-300℃). This mode is mostly used for geometrical parts with standard product appearance models. Internal cooling pipes arranged in straight lines are designed on the mold, and the heat energy is directly taken away with cooling water to obtain temperature balance. The flow rate can also be adjusted slightly for partial parts. At present, there are many applications, but there are also some problems.
(2) According to the temperature field, the targeted design area is simulated, and the temperature balance is achieved by partial cooling. Among them, the point cooling method is used more in protruding hot parts of the forming cavity of the mold. A new design pattern is proposed based on the practical experience.
2. The general traditional point cooling design
The traditional point cooling design is shown in the Figure 1. The cooler is connected with the workpiece by threads, and the cooler is screwed into the workpiece. Because the PT thread is adopted, there is no leakage between the cooler and workpiece, and the cooler pipe penetrates the cooling hole of the workpiece. When the cooling water is connected, the water is ejected through the center pipe of the cooler, so that the cooling water circulates in the cooling hole of the workpiece.
Figure 1 The traditional point cooling method
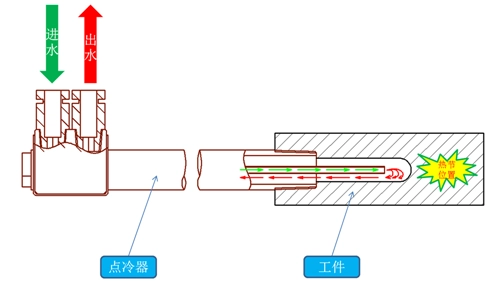
Water circulation is formed inside the point cooler, and the cooling water takes away the heat at the bottom of the hole, which can reduce the size of the hot joint on the workpiece. In this way, the temperature balance in the partial area can be effectively realized, and the process is mature. However, it can not be effectively applied to the parts with limited outer diameters. When it is necessary to ensure the strength of wall thickness of molds, super point cooling with Φ2 to 4mm can only be used for the bottom hole. After design and manufacturing, the effect is not ideal due to the influence of structural space and water pressure, as shown in the Figure 2.
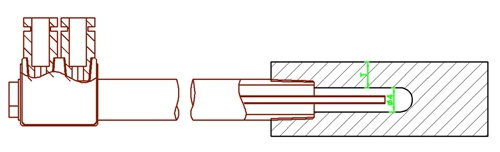
Figure 2 Wall thickness of mold cooling
3. Choosing materials with good heat transfer effect
Graphene materials with excellent unidirectional thermal conductivity are selected as the conductor. Graphene is relatively brittle, so the metal silver with good thermal conductivity is selected as the matrix. Graphene is deposited on the metal silver through physical vapor phase deposition. The following device is designed to sift a variety of materials and record the process with a thermometer, as shown in the Figure 3.
Figure 3 Sifting the test device for thermal conductive materials
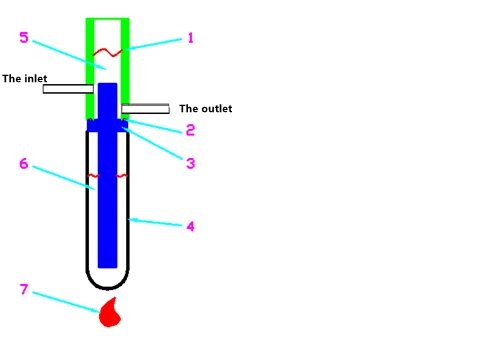
1. Glass tubes 2. Sealing rings 3. Conductors 4. Test tubes 5. Cooling water 6. Boiling water 7. Fire
The test results are shown in the Table 1. It can be seen that silver with graphene has the best thermal conductivity.
Table 1 A comparison of thermal conductivity of different materials
4. Design and verification of the new super point cooling structure
According to the test results, a mold insert was selected for specific verification. See the figure 4 for the partial point cooling design on the mold.
Figure 4 The new structure of super point cooling
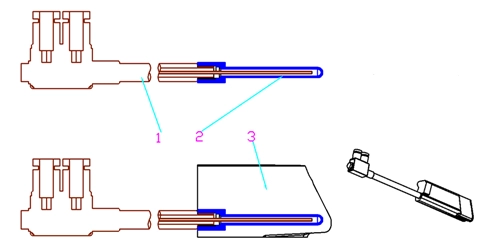
1. Point cooler 2. Conductors 3. Workpieces
The metal silver sleeve with graphene is inserted into the workpiece, and the point cooler is inserted into the metal sleeve. The point cooler cools the graphene conductor, and the graphene conductor cools the workpiece, thus achieving the purpose of workpiece of cold zones. It can be used for cooling small workpieces; even if the insert is damaged, the cooling water will not flow into the product, resulting in the scrap of the product. It was found that the effective life of the insert was increased from the range of 15,000-20,000 times to that of 30,000 and 40,000 times, and the effect was good.
5. Conclusion
The new type of point cooler can effectively solve the leakage problem of the die core caused by the cracking of the die core, improve the production efficiency, save the production cost and increase the use range of the point cooling structure.
Under the trend of energy saving and emission reduction, the automobile lightweight has attracted more and more attention. Using aluminum alloys instead of steel structure, the development of traditional automobile lightweights and new energy vehicles have been more and more applied. A die casting mould as the key tool in die casting process, its effective life is very important to reduce the product cost. Thermal alternating stress fatigue caused by the temperature imbalance of the forming surface of the die is the main factor of die failures.
1. The way to solve the temperature imbalance
(1) For die castings, the temperature difference is reduced by effective output of input energy (The energy emitted by the aluminum alloy melt with temperatures from 650℃±10℃ to 200℃-300℃). This mode is mostly used for geometrical parts with standard product appearance models. Internal cooling pipes arranged in straight lines are designed on the mold, and the heat energy is directly taken away with cooling water to obtain temperature balance. The flow rate can also be adjusted slightly for partial parts. At present, there are many applications, but there are also some problems.
(2) According to the temperature field, the targeted design area is simulated, and the temperature balance is achieved by partial cooling. Among them, the point cooling method is used more in protruding hot parts of the forming cavity of the mold. A new design pattern is proposed based on the practical experience.
2. The general traditional point cooling design
The traditional point cooling design is shown in the Figure 1. The cooler is connected with the workpiece by threads, and the cooler is screwed into the workpiece. Because the PT thread is adopted, there is no leakage between the cooler and workpiece, and the cooler pipe penetrates the cooling hole of the workpiece. When the cooling water is connected, the water is ejected through the center pipe of the cooler, so that the cooling water circulates in the cooling hole of the workpiece.
Figure 1 The traditional point cooling method

Water circulation is formed inside the point cooler, and the cooling water takes away the heat at the bottom of the hole, which can reduce the size of the hot joint on the workpiece. In this way, the temperature balance in the partial area can be effectively realized, and the process is mature. However, it can not be effectively applied to the parts with limited outer diameters. When it is necessary to ensure the strength of wall thickness of molds, super point cooling with Φ2 to 4mm can only be used for the bottom hole. After design and manufacturing, the effect is not ideal due to the influence of structural space and water pressure, as shown in the Figure 2.

Figure 2 Wall thickness of mold cooling
3. Choosing materials with good heat transfer effect
Graphene materials with excellent unidirectional thermal conductivity are selected as the conductor. Graphene is relatively brittle, so the metal silver with good thermal conductivity is selected as the matrix. Graphene is deposited on the metal silver through physical vapor phase deposition. The following device is designed to sift a variety of materials and record the process with a thermometer, as shown in the Figure 3.
Figure 3 Sifting the test device for thermal conductive materials

1. Glass tubes 2. Sealing rings 3. Conductors 4. Test tubes 5. Cooling water 6. Boiling water 7. Fire
The test results are shown in the Table 1. It can be seen that silver with graphene has the best thermal conductivity.
Table 1 A comparison of thermal conductivity of different materials
| BeCu | Metallic silver |
Stainless steel |
Graphene coated silver | |
| Required time for reaching the boiling water state/s | 256 |
500 |
200 |
560 |
4. Design and verification of the new super point cooling structure
According to the test results, a mold insert was selected for specific verification. See the figure 4 for the partial point cooling design on the mold.
Figure 4 The new structure of super point cooling

1. Point cooler 2. Conductors 3. Workpieces
The metal silver sleeve with graphene is inserted into the workpiece, and the point cooler is inserted into the metal sleeve. The point cooler cools the graphene conductor, and the graphene conductor cools the workpiece, thus achieving the purpose of workpiece of cold zones. It can be used for cooling small workpieces; even if the insert is damaged, the cooling water will not flow into the product, resulting in the scrap of the product. It was found that the effective life of the insert was increased from the range of 15,000-20,000 times to that of 30,000 and 40,000 times, and the effect was good.
5. Conclusion
The new type of point cooler can effectively solve the leakage problem of the die core caused by the cracking of the die core, improve the production efficiency, save the production cost and increase the use range of the point cooling structure.